/ What is VPN and its Applications
VPN, which means "Virtual Private Network," is a service that protects your Internet connection as well as your online privacy. By hiding your IP address, this service will create an encrypted tunnel for your data, not only protecting your online identity, but also allowing you to use public Wi-Fi hotspots safely.
The three types of VPN:
1.SSL VPN
2.Site-to-Site VPN
3.Client to Server VPN
Why you need use VPN?
When you connect to the Internet, your ISP usually sets up your connection, which tracks you by IP address. Your web traffic is routed through your ISP's server, which records and displays everything you do online.
Your ISP may appear trustworthy, but they may share your browsing history with advertisers, the police or government or other third parties. ISPs can also fall victim to cybercriminals: if they get hacked, your personal and private data can be leaked.
This is especially important if you frequently connect to public Wi-Fi networks. You never know who might be monitoring your internet traffic and what they might be stealing from you, including passwords, personal data, payment information, and even your entire identity.
The working principle of VPN:
1.When you connect to a virtual private network service (VPN), it will authenticate the client through the VPN server.
2.After that, the server will apply an encryption protocol to all the data you send and receive.
3.The VPN service will create an encrypted "tunnel" over the Internet. This tunnel will protect the data in transit between you and the destination.
4.To ensure the security of each packet, the VPN wraps it in an outer packet, then encrypted by encapsulation. The outer packet is the core element in the VPN tunnel, which will ensure the security of the data in transit.
5.When the data arrives at the server, through the decryption process, the outer packets will be removed.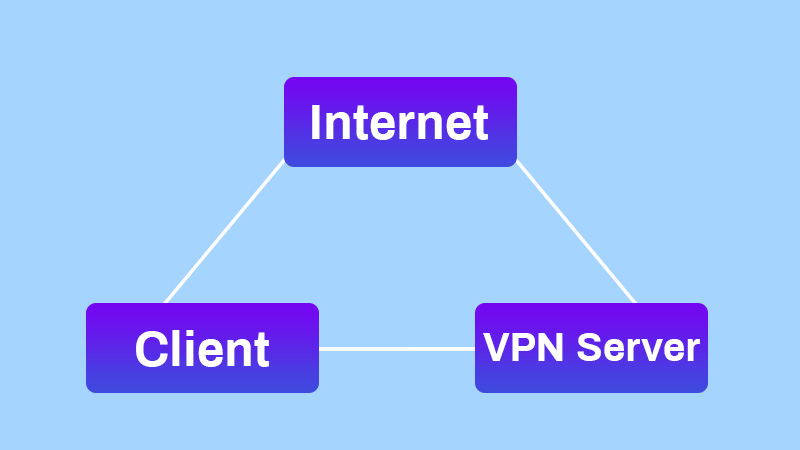
The benefits of VPN connection:
A VPN connection can hide your data traffic online and protect it from outside access. Unencrypted data can be viewed by anyone who has internet access and wants to see the data. With a VPN, hackers and cybercriminals cannot decipher these data.
Secure Encryption: To read data, you need an encryption key. Without the security key, it would take a computer millions of years to decipher the code by brute force. With the help of VPN, your online activities on public networks will be hidden.
Disguising your location: VPN servers actually act as your proxy on the Internet. Your actual location cannot be determined because the statistical location data comes from servers in other countries. Also, most VPN services do not store logs of your activity. On the other hand, some providers will log your actions but do not pass the information to the third parties. It means that any potential records of user behavior are permanently hidden.
Access to regional content: Regional web content is not always accessible everywhere. Services and websites tend to contain content that can only be accessed from certain parts of the world. Standard connections use the local server in your country to determine your location. This means you can't access content from your hometown when you travel, nor can you access international content at home. With VPN location spoofing, you can switch to a server in another country and "change" your location efficiently.
Secure data transfer: If you work remotely, you may need to access important files on your company network. For security, the information requires a secure connection. In order to gain access to the network, the VPN connection is usually required. VPN services connect to dedicated servers and use encryption to reduce the risk of data leakage.